Language Arts: Correct Spelling and Understanding the Subject
How to spell language arts right
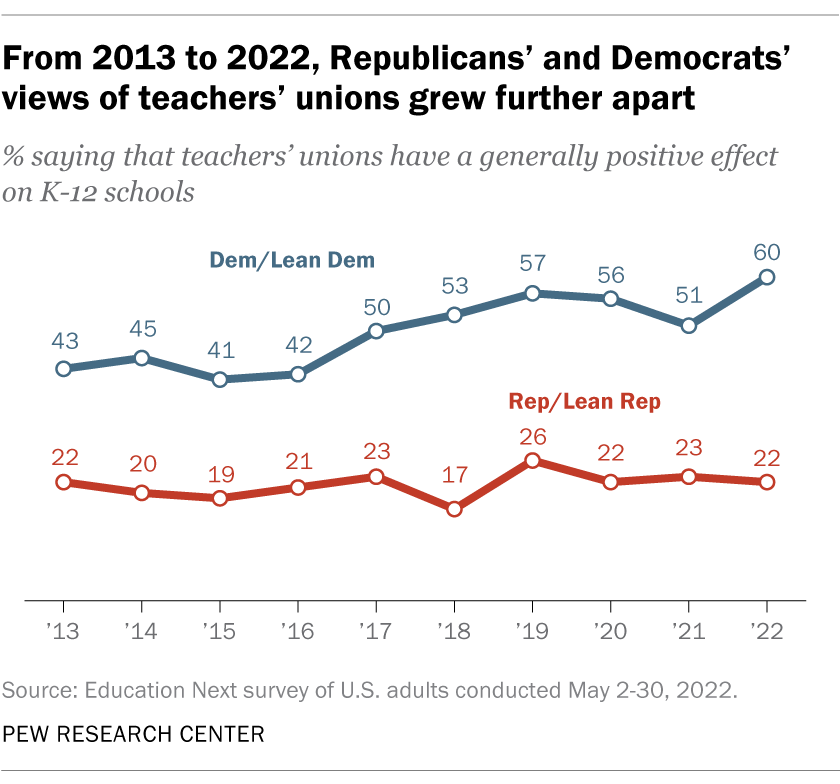
The correct spelling of” language arts” is precisely that — language arts. It consists of two words:” language” and” arts. ” Both words begin with capital letters when refer to the academic subject, though in general text they may be written in lowercase as” language arts. ”
Common misspellings include:
- Language arts (transpose the’ u’ and’ a’ )
- Language arts( omit the’ u’)
- Language art (omit the’s’ in arts )
- Language arts (substitute’ i’ for’ a’ )
What just is language arts?
Language arts is a core academic subject that encompass various aspects of language study and communication skills. It’s an integrated approach to learn about language and develop proficiency in its use across multiple contexts.
The term” language arts ” s chiefly use in noNorth Americanducation systems, while some other enEnglishpeak countries might refer to similar studies as “” gEnglish” ” e” iEnglishuage. ”
Components of language arts
Language arts is not a single skill, but preferably a collection of interconnect language competencies include:
Read
Read instruction focus on decode text, comprehension strategies, literary analysis, and develop a love for literature. Students learn to identify themes, analyze characters, understand plot structures, and interpret various text types from fiction to informational writing.
Write
Write instruction cover everything from basic mechanics (spelling, grammar, punctuation )to composition skills. Students learn different writing formats include narrative, expository, persuasive, and descriptive writing. The writing process — prewriting, drafting, revising, editing, and publishing — form the backbone of writing instruction.
Speak
Oral communication skills include public speaking, debate, discussion, presentation skills, and conversational abilities. Students learn to articulate ideas intelligibly, adapt their speak style to different audiences, and use verbal and non-verbal cues efficaciously.

Source: giftedguru.com
Listen
Active listening involve comprehend speak language, follow directions, distinguish important information, and respond befittingly. This oftentimes overlook component is crucial for classroom learning and social interaction.
View
In the modern curriculum, view involve critically analyze visual media, include films, advertisements, websites, and graphic representations. Students learn to interpret visual information and understand how images communicate meaning.
Represent
This involves create visual, audio, or multimedia presentations to communicate ideas. Students learn to select appropriate media and design effective presentations for various purposes and audiences.
Grammar and mechanics
Understand the structure of language is a fundamental aspect of language arts. This includes:
- Parts of speech (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc. )
- Sentence structure and syntax
- Punctuation rules
- Spell patterns and conventions
- Paragraph and essay structure
Literature study
Explore literature from various genres, time periods, and cultures is a significant component of language arts. Through literature, students:

Source: pcartlidgetks.weebly.com
- Develop cultural awareness and empathy
- Recognize literary devices and techniques
- Analyze themes and author’s purpose
- Make connections between texts and their own lives
- Develop critical thinking skills
The importance of language arts in education
Language arts is considered a foundational subject for several important reasons:
Cross curricular applications
The skills develop in language arts transfer to all other academic areas. Strong reading comprehension help students understand math word problems, science texts, and historical documents. Write skills enable students to communicate their knowledge in any subject. Speak and listen facilitate participation in class discussions across all disciplines.
Critical thinking development
Language arts instruction encourage analytical thinking, evaluation of information, and reason argument — all essential components of critical thinking. When students analyze literature, debate perspectives, or craft persuasive essays, they’re developed higher order thinking skills.
Communication in the digital age
Despite technological advances, or possibly because of them, communication skills remain vital. Language arts instruction has evolved to include digital literacy, teach students to navigate, evaluate, and create content in various digital formats while maintain strong traditional language skills.
Cultural literacy and empathy
Through exposure to diverse literature and perspectives, language arts help students develop cultural understanding and empathy. Read stories from different cultures and time periods allow students to experience lives and viewpoints different from their own.
Language arts across grade levels
Elementary language arts (k 5 )
In early elementary grades, language arts focus on foundational literacy skills:
- Phonemic awareness and phonics
- Sight word recognition
- Basic reading comprehension
- Handwriting and early composition
- Oral language development
As students progress through elementary school, the focus shifts to more complex skills:
- Read fluency and advanced comprehension strategies
- Paragraph and multi paragraph writing
- Basic research skills
- Grammar and spelling conventions
- Literary analysis of grade appropriate texts
Middle school language arts (6 8)
Middle school language arts build on elementary foundations while prepare students for high school:
- More sophisticated literary analysis
- Introduction to different essay formats
- Research papers with citations
- Advanced grammar concepts
- Public speaking and presentation skills
- Media literacy
High school language arts (9 12 )
High school English or language arts courses typically include:
- In depth literary analysis across genres and time periods
- Advanced composition, include college level essays
- Research methodology and academic writing
- Rhetorical analysis and argumentation
- Creative writing
- Critical theory and approaches to literature
Effective language arts instruction
Integrated approach
Modern language arts instruction typically takes an integrated approach, recognize that reading, writing, speak, and listening are interconnect. Quite than teach these skills in isolation, effective teachers create learning experiences that combine multiple language processes.
Balanced literacy
A balanced literacy approach incorporate both explicit skill instruction and authentic reading and write experiences. This includes:
- Direct instruction in specific skills
- Guide practice with teacher support
- Independent application of skills
- Meaningful context for language use
Differentiate instruction
Recognize that students have different strengths, needs, and learn styles, effective language arts teachers differentiate instruction by:
- Offer texts at various reading levels
- Provide multiple ways to demonstrate learn
- Adjust the level of support base on student needs
- Create flexible grouping arrangements
Technology integration
Digital tools have transformed language arts instruction, offer new ways to engage with language:
- Digital read platforms with build in supports
- Write tools with feedback features
- Multimedia creation for projects
- Online collaboration opportunities
- Access to diverse texts and resources
Support language arts development at home
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in language development. Effective strategies include:
Create a literature rich environment
- Maintain a home library with diverse reading materials
- Read loudly to children, regular after they can read severally
- Modeling reading for pleasure
- Discuss books and stories as a family
Encourage authentic writing
- Provide opportunities for real world writing (letters, journals, blogs )
- Celebrate write efforts
- Help with the editing process when ask
- Share family stories and encourage children to record them
Promote rich conversation
- Engage in discussions that go beyond yes / no questions
- Introduce new vocabulary in context
- Encourage children to express opinions and support them with reasons
- Play word games and tell stories
Common challenges in language arts
Read difficulties
Many students struggle with aspects of reading, from decode to comprehension. Early intervention is key, as read difficulties can impact all academic areas. Approaches may include:
- Structured phonics instruction
- Explicit comprehension strategy teaching
- Regular guide reading in appropriate texts
- Multisensory learn approach
Write reluctance
Some students develop anxiety or resistance toward write tasks. Effective strategies include:
- Break write into manageable steps
- Provide choice in write topics
- Create authentic purposes for write
- Focus on ideas before mechanics
- Use technology to support the writing process
English language learners
Students learn English face additional challenges in language arts. Supportive approaches include:
- Build on first language strengths
- Provide visual supports and context
- Explicitly teach academic language
- Allow multiple ways to demonstrate understand
- Celebrate bilingualism as an asset
The future of language arts education
Language arts continue to evolve in response to change communication landscapes and educational research:
Digital literacy integration
As digital texts and media become progressively central to communication, language arts instruction is expanded to include skills like:
- Evaluate online sources
- Understand digital text feature
- Create multimedia presentations
- Navigate digital reading environments
- Participate in online discourse fittingly
Culturally responsive teaching
Language arts education is progressively recognized the importance of cultural relevance:
- Diversify literature selections
- Validate students’ linguistic backgrounds
- Connect curriculum to students’ live experiences
- Examine language through cultural and historical lenses
Interdisciplinary approaches
The boundaries between subject areas are become more fluid, with language arts skills apply across disciplines:
- Content area literacy strategies
- Project base learning span multiple subjects
- Integration of arts and language
- Stem relate reading and write
Conclusion
Language arts — aright spell with both words capitalize when refer to the subject area — encompass a wide range of interconnect language and communication skills. From the foundational abilities to read and write to the higher order skills of analysis and creation, language arts provide students with essential tools for academic success and lifelong learning.
As communication continue to evolve in our digital world, strong language arts skills remain crucial. The ability to comprehend complex texts, express ideas intelligibly in writing, speak efficaciously to various audiences, and critically evaluate information are timeless competencies that serve individuals throughout their lives.
Whether you’re a student work to master these skills, a parent support language development at home, or an educator design effective instruction, understand the comprehensive nature of language arts is the first step toward language proficiency.